Cluster Mode Overview
공부하면서 기록한것, 틀린 해석이 있을수 있음.
원문 ; https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html
Cluster Mode Overview
This document gives a short overview of how Spark runs on clusters, to make it easier to understand the components involved. Read through the application submission guide to submit applications to a cluster.
이 문서는 스파크를 쉽게 관련 구성 요소를 이해하기위해 클러스터에서 어떻게 실행시기는지 짧은 개요를 설명한다. 클러스터에 어플을 제출하기 위해 어플 제출가이드를 읽어라.
Components
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program (called the_driver program_). Specifically, to run on a cluster, the SparkContext can connect to several types of cluster managers (either Spark’s own standalone cluster manager or Mesos/YARN), which allocate resources across applications. Once connected, Spark acquires executors on nodes in the cluster, which are processes that run computations and store data for your application. Next, it sends your application code (defined by JAR or Python files passed to SparkContext) to the executors. Finally, SparkContext sends tasks for the executors to run.
스파크 응용프로그램은 네놈의 메인 프로그램(driver 프로그램이라고 부른다.)안에서 SparkContext 객체에 의해 통합된, 클러스터에서 독립적인 프로세스 집합을 실행한다. 명확하게, 클러스터에서 실행하는 것은, SparkContext 는 클러스터 매니저들의 몇몇 타입에 연결할 수 있고(Spark의 standalone 클러스터 관리자 또는 Mesos/YARN), 응용프로그램에 거쳐서 자원을 할당할 수 있다. 한번 연결되어지면, 스파크는 네놈의 응용프로그램에 대한 연산과 데이터 저장을 처리하는 executor 를 클러스터에 속한 노드에서 취득한다. 다음으로, 네놈의 응용프로그램 코드를 executor 들에게 전송한다. 마지막으로, SparkContext 는 executor 가 실행하기 위한 tasks 를 보낸다.
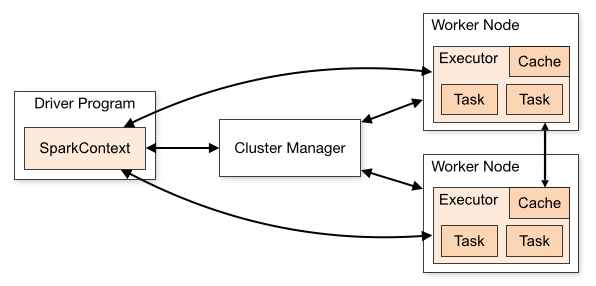
There are several useful things to note about this architecture:
이 아키텍처에서 주의해야 할 몇 가지 유용한 것들 :
-
Each application gets its own executor processes, which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads. This has the benefit of isolating applications from each other, on both the scheduling side (each driver schedules its own tasks) and executor side (tasks from different applications run in different JVMs). However, it also means that data cannot be shared across different Spark applications (instances of SparkContext) without writing it to an external storage system.
-
Spark is agnostic to the underlying cluster manager. As long as it can acquire executor processes, and these communicate with each other, it is relatively easy to run it even on a cluster manager that also supports other applications (e.g. Mesos/YARN).
-
Because the driver schedules tasks on the cluster, it should be run close to the worker nodes, preferably on the same local area network. If you’d like to send requests to the cluster remotely, it’s better to open an RPC to the driver and have it submit operations from nearby than to run a driver far away from the worker nodes.
-
각 응용프로그램은 자신의 executor 프로세스들을 획득하고, 그것은 멀티스레드에서 전체 응용프로그램과 실행 tasks 의 지속시간 동안 대기한다.이것은 스케줄링 측( 각 드라이버 일정 자신의 작업 )과 executor 측( 다른 응용프로그램으로 부터의 tasks 는 다른 JVMs에서 실행 ) 모두 서로 응용 프로그램을 분리하는 장점이 있다. 그러나, 그것은 또한 데이터는 다른 Spark 응용 프로그램 (SparkContext의 인스턴스) 을 거쳐 외부 저장 시스템으로 쓰기 없이 공유할 수 없다는 뜻이다.
-
Spark 는 기본 클러스터 관리자에 얽매이지 않는다. 오랫동안 executor 프로세스를 획득할 수 있고, 이들이 서로 통신하고 , 그것은 비교적 쉽다 클러스터 관리자에서 실행하는 . executor를 획득, executor 간 통신하는 것을 클러스터 관리자에서 실행하는 것은 비교적 쉽다. 또한 다른 응용프로그램도 지원한다. (Mesos/YARN) ;;;;;;
-
드라이버는 클러스터에서 tasks 일정을 만들기 때문에, 가까운 worker 노드에서 실행해야 하고, 동일한 로컬영역 네트웍이 바람직하다. 만약 원격 클러스터로 요청을 보내야 할 경우, 드라이버에게 RPC를 열고, 멀리 있는 worker 노드에서 드라이버를 실행하는 것 보다 근처의 worker 노드로 명령을 제출하는것이 좋다.’;;;;
Cluster Manager Types
The system currently supports three cluster managers:
시스템이 현재 지원하는 세가지 클러스터 관리자:
-
Standalone – a simple cluster manager included with Spark that makes it easy to set up a cluster.
-
Apache Mesos – a general cluster manager that can also run Hadoop MapReduce and service applications.
-
Hadoop YARN – the resource manager in Hadoop 2.
In addition, Spark’s EC2 launch scripts make it easy to launch a standalone cluster on Amazon EC2.
Submitting Applications
Applications can be submitted to a cluster of any type using the spark-submit script. The application submission guide describes how to do this.
Monitoring
Each driver program has a web UI, typically on port 4040, that displays information about running tasks, executors, and storage usage. Simply go to http://
각 드라이버 프로그램은 web UI 를 가지고 있고, 일반적으로 4040 포트를 사용, 그것은 실행중인 tasks 에 관한 정보, 저장 용량 사용량을 표출한다.
간단하게 웹 브라우저에서 http://
Job Scheduling
Spark gives control over resource allocation both across applications (at the level of the cluster manager) and within applications (if multiple computations are happening on the same SparkContext). The job scheduling overview describes this in more detail.
스파크는 전체 응용 프로그램 및 응용 프로그램의 리소스 할당을 제어( 클러스터 관리자 수준에서 )할 수 있다. ( 여러 계산이 같은 SparkContext에서 일어 나고 있는 경우 ). job scheduling overview 여기를 봐라;;
Glossary
The following table summarizes terms you’ll see used to refer to cluster concepts:
Term
Meaning
Application
User program built on Spark. Consists of a driver program and executors on the cluster.
스파크에 구축된 사용자 프로그램. 클러스터의 _driver _프로그램과 _executor _의 구성
Application jar
A jar containing the user’s Spark application. In some cases users will want to create an “uber jar” containing their application along with its dependencies. The user’s jar should never include Hadoop or Spark libraries, however, these will be added at runtime.
사용자의 스파크 응용프로그램을 포함하는 jar. 해당 jar 에는 Hadoop 또는 Spark libraries를 절대 가지고 있으면 안된다.
Driver program
The process running the main() function of the application and creating the SparkContext
Cluster manager
An external service for acquiring resources on the cluster (e.g. standalone manager, Mesos, YARN)
Deploy mode
Distinguishes where the driver process runs. In “cluster” mode, the framework launches the driver inside of the cluster. In “client” mode, the submitter launches the driver outside of the cluster.
Worker node
Any node that can run application code in the cluster
클러스터의 응용 프로그램 코드를 실행 할 수 있는 모든 노드
Executor
A process launched for an application on a worker node, that runs tasks and keeps data in memory or disk storage across them. Each application has its own executors.
worker 노드에서 응용 프로그램을 위해 tasks 를 실행하고 메모리 또는 디스크 저장소 에 데이터 유지하는, worker 노드에서 응용 프로그램을 위해 실행되는 프로세스. 각 응용 프로그램은 자신의 executor를 갖는다.
Task
A unit of work that will be sent to one executor
하나의 executor 에게 보내질 작업의 단위.
Job
A parallel computation consisting of multiple tasks that gets spawned in response to a Spark action (e.g. save, collect); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs.
스파크 action ( 예 save, collect )에 반응하여 생성된 여러 tasks 로 구성된 병렬 연산; 네놈은 드라이버의 로그에서 이 용어가 사용된 것을 볼것이다.
Stage
Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs.
각 Job 은 서로 종속적인 ( MapReduce의 map 과 reduce states와 유사한) _stages _라 불리는 tasks 의 작은 집합으로 분할된다;
- [정리] 정보이론: 정보량 (Information), 엔트로피 ( Entropy ), 쿨백 라이블러 발산 (KL-Divergence), 크로스 엔트로피 ( Cross - Entropy ), maximum likelihood
- [발번역] Bag of words (BoW) - Natural Language processing
- Installing Anaconda and Jupyter notebook
- 다시 보는 Java : FileChannel transferTo()
- 다시 보는 Java : NIO Channel
- 다시 보는 Java : Socket-Direct-Protocol
- 다시 보는 Java
- Streamsets DataCollector Source Build
- Apache Helix Core Concepts
- Introduce Flipkart Aesop





